BACKGROUND
Cloud computing offers on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, delivering hosted services over the internet. In data storage, Multi-tenancy in cloud computing makes a greater pool of resources available to a larger group of people without sacrificing privacy & security or slowing down applications. Multi-tenant environment allows a group of people all share access to the hardware memory through the underlying software.
For instance: 1. A service provider may offer a hosted private cloud service to its customers in which each tenant has administrative access to its own instance of vCenter and a set of dedicated ESXi hosts, but underlying storage resources are shared. 2. For large enterprise companies, IT organizations may create an enterprise cloud in which they can dedicate resources to meet the IT needs of internal “tenants” such as development teams or line-of-business teams.
OVERVIEW
- My Role Lead UX designer
- Target User Virtualization & Storage Engineers work at Cloud Service Providers hosted private cloud service and enterprises with private cloud infrastructure.
- Product Category Data Storage Solutions for Enterprise Cloud
- Length of the Project Jan - Apr 2017, (Launched in Nov 2017)
GOAL
Streamline user experience to allow Service Providers to monitoring all space usage and have full control over how much total space a tenant can consume and make it simple to limit capacity available to each tenant in the multi-tenant environments.
PROBLEMS

No full control over storage capacity limit
Service Provider would like to charge end customers for the space they used but they didn’t have full control to manage their customers quotas and capacity.

No warnings prior storage over capacity
Service Providers didn’t receive warnings until their customers reach quota limit, which could be a dangerous situation since VMs can crash when writes start to fall.
USE CASE
Set capacity limit on total consumption for each tenant to adjust capacity limits up or down on the fly.
As a Data Storage Service Provider, I want to ensure that different tenants don't consume more capacity than they are allowed.
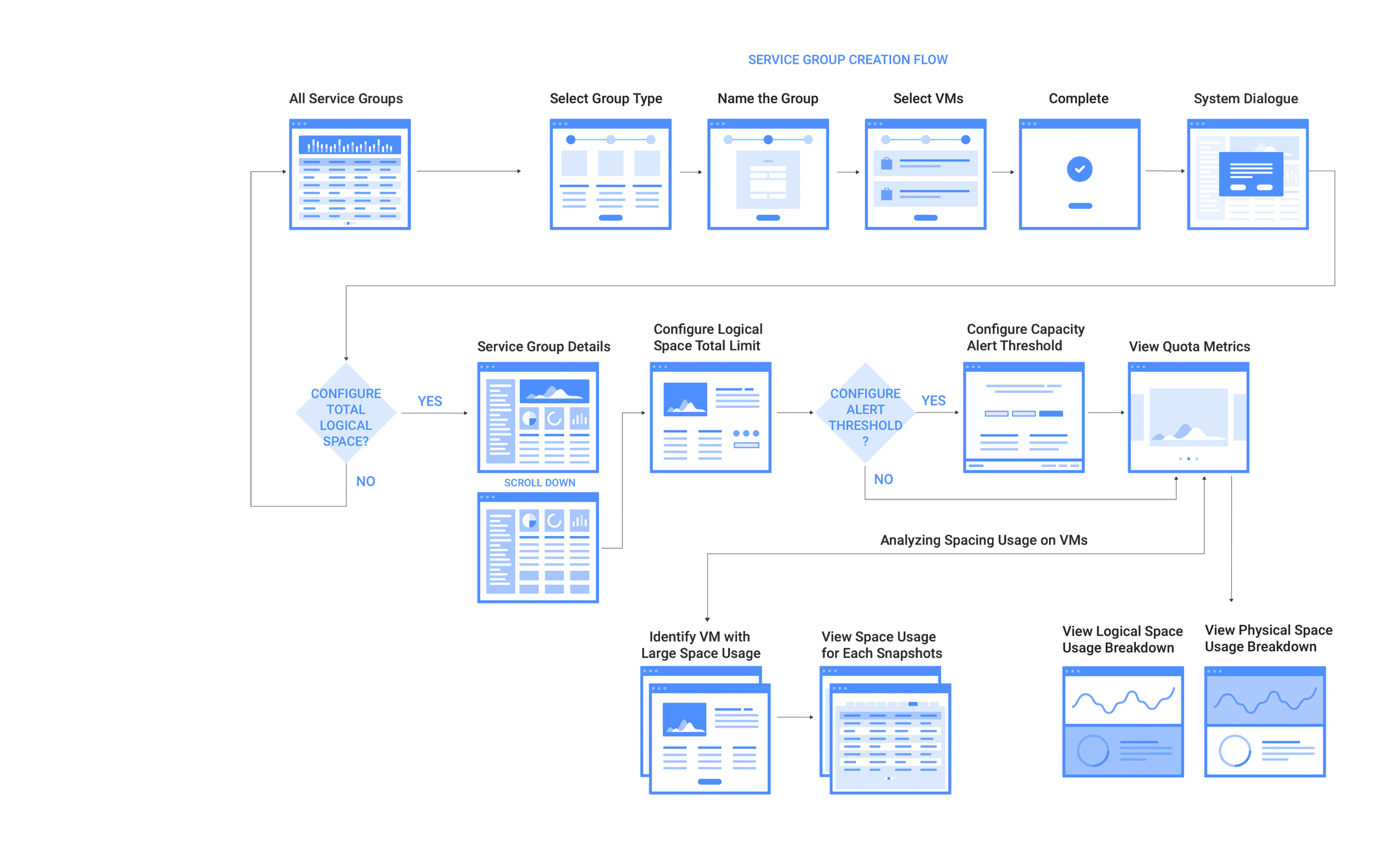
DESIGN EXPLORATION
Data Visualization on Space Management
After few rounds of flow discussion, we finalized the interaction flows per use case requirement. I started to work on mock ups, I took a step back to analyze what exactly we wanted to show, what is the main purpose of this design, and what the user would find most helpful in Space Management? Realizing how easy it is to put everything but the most important data into a new feature, I asked end users, what is the key information they need to see when manage space capacity? And what we kept hearing was: "How much space do I have left in my VMstores? How much data I used in snapshots, how much space in live data? What's my space savings factors? This is is how we decided to make "How am I doing" the focal point. Let the user see how they compare current space usage with the target space quota threshold, and give them indicators of which VMs or VMstores might need their attention, from there, they can drill down to the details and see performance stats. That way, they know where to make adjustments so they can avoid over space capacity.
SOLUTIONS
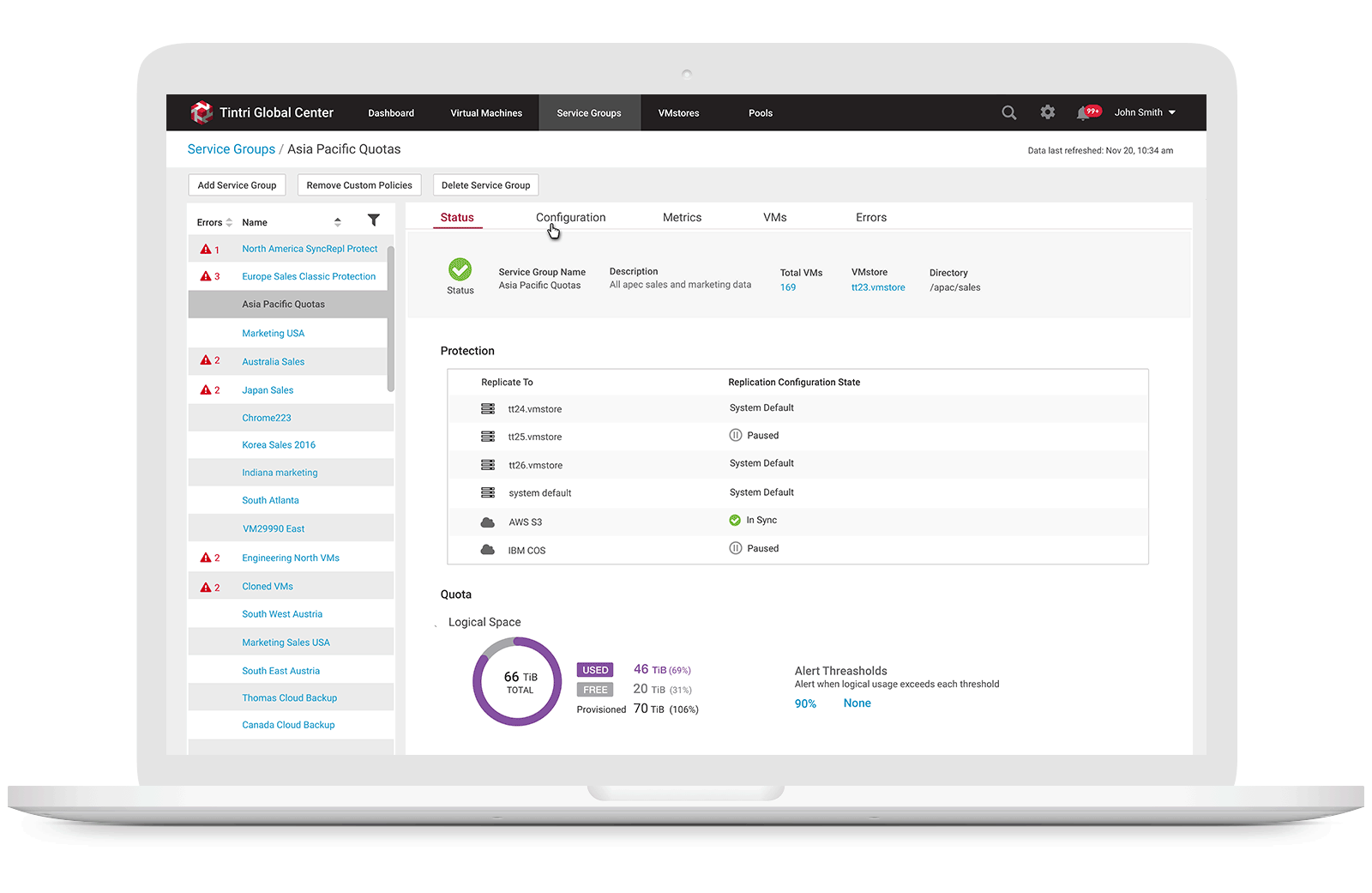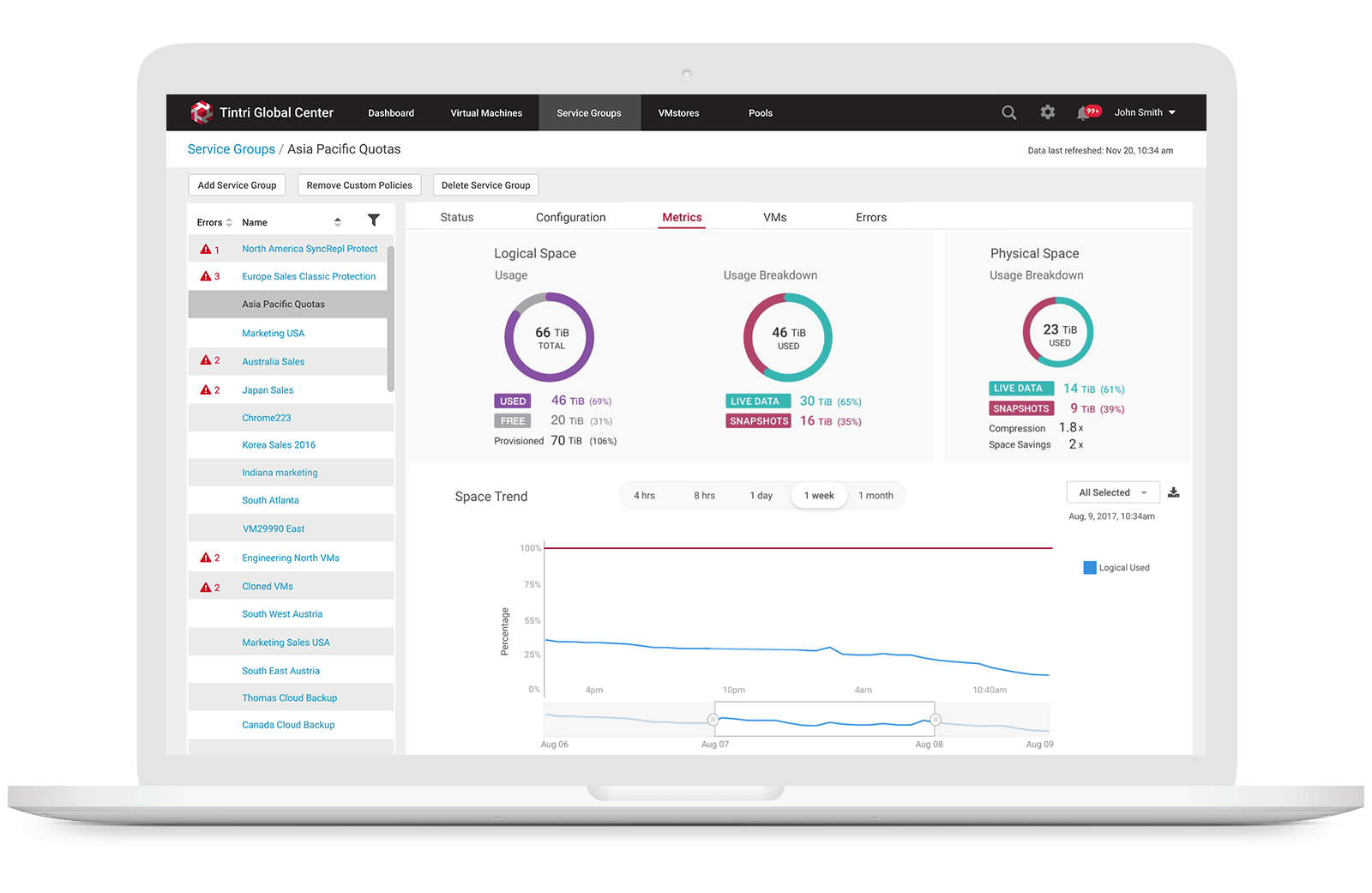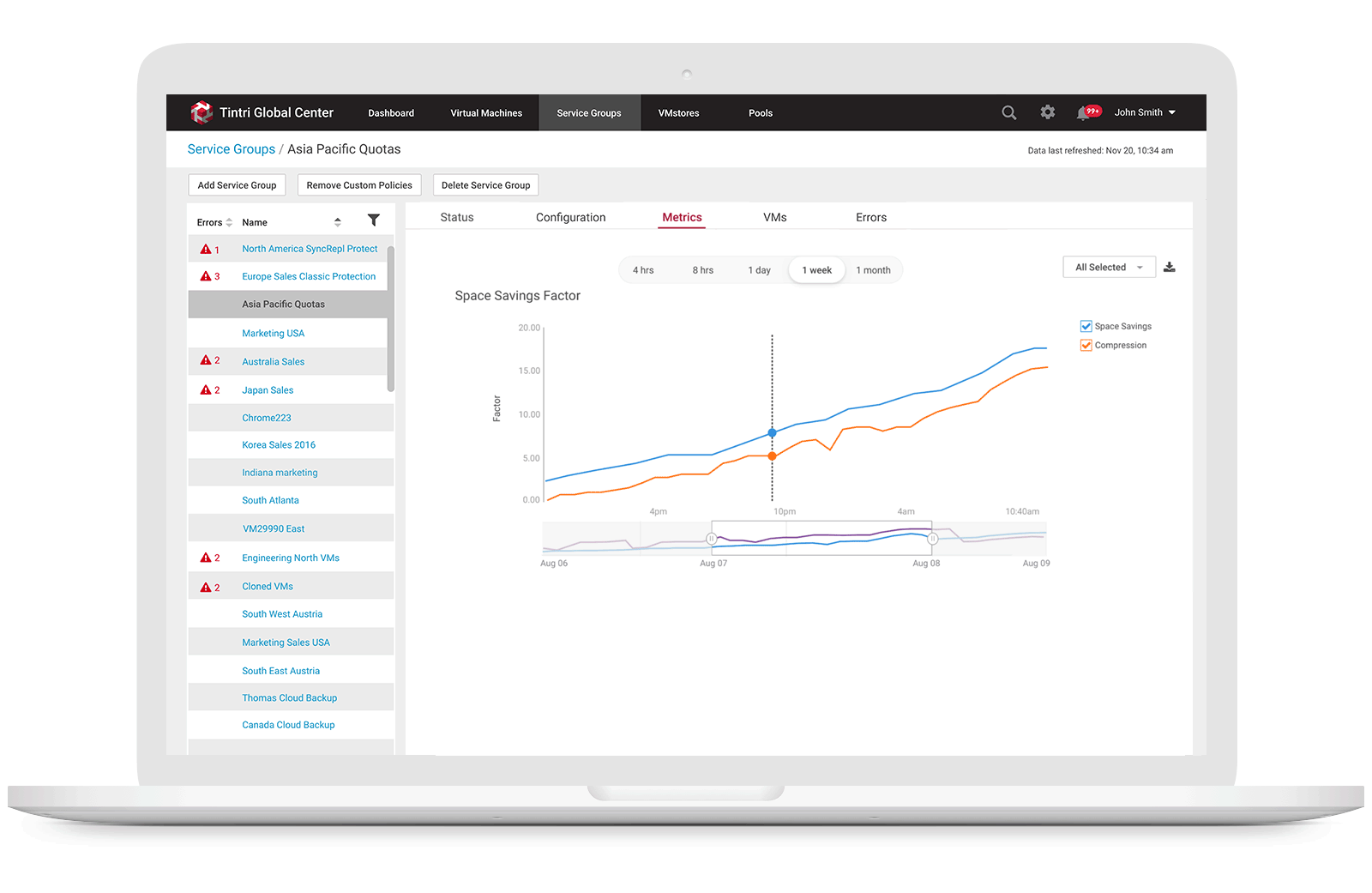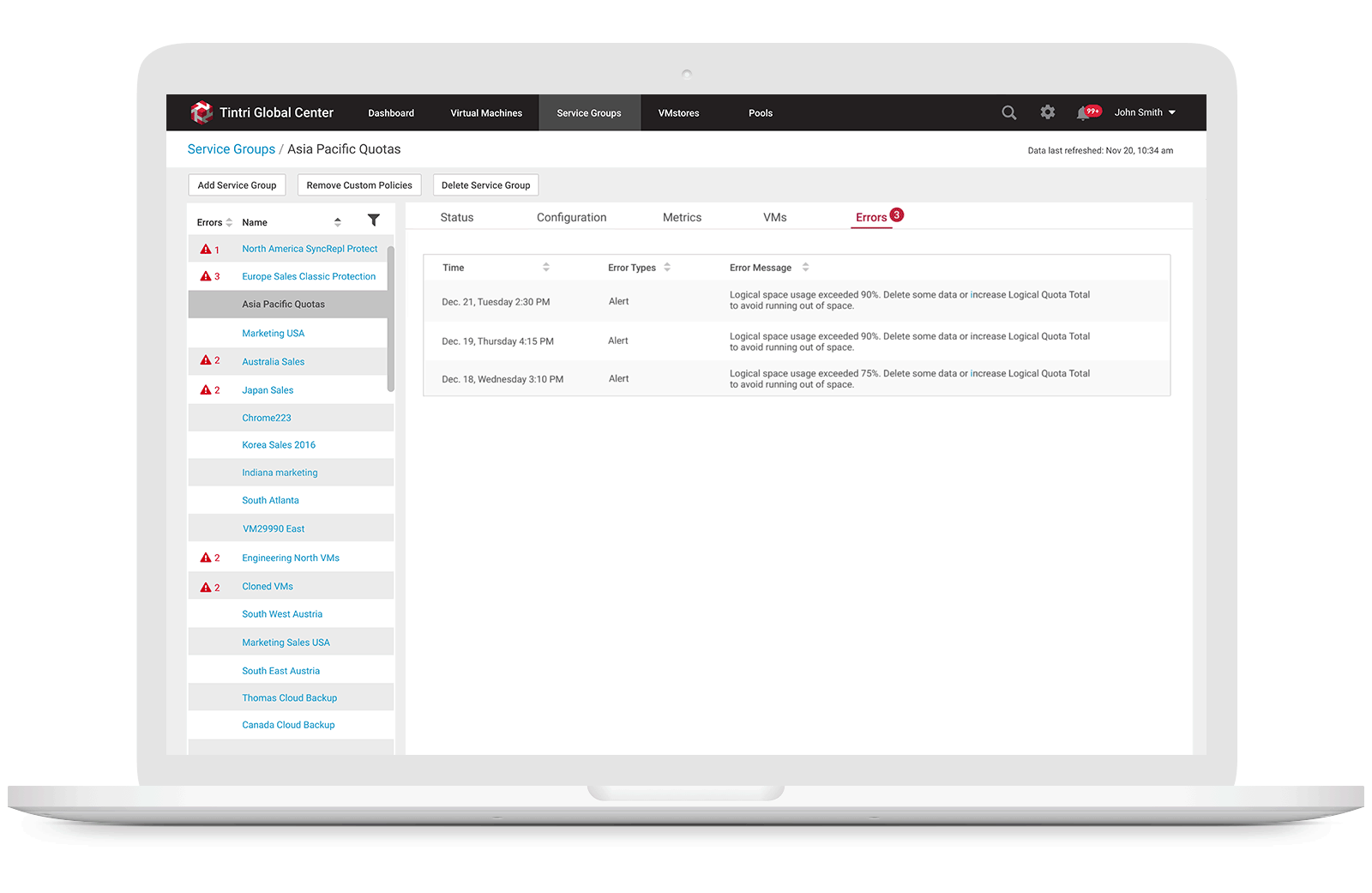
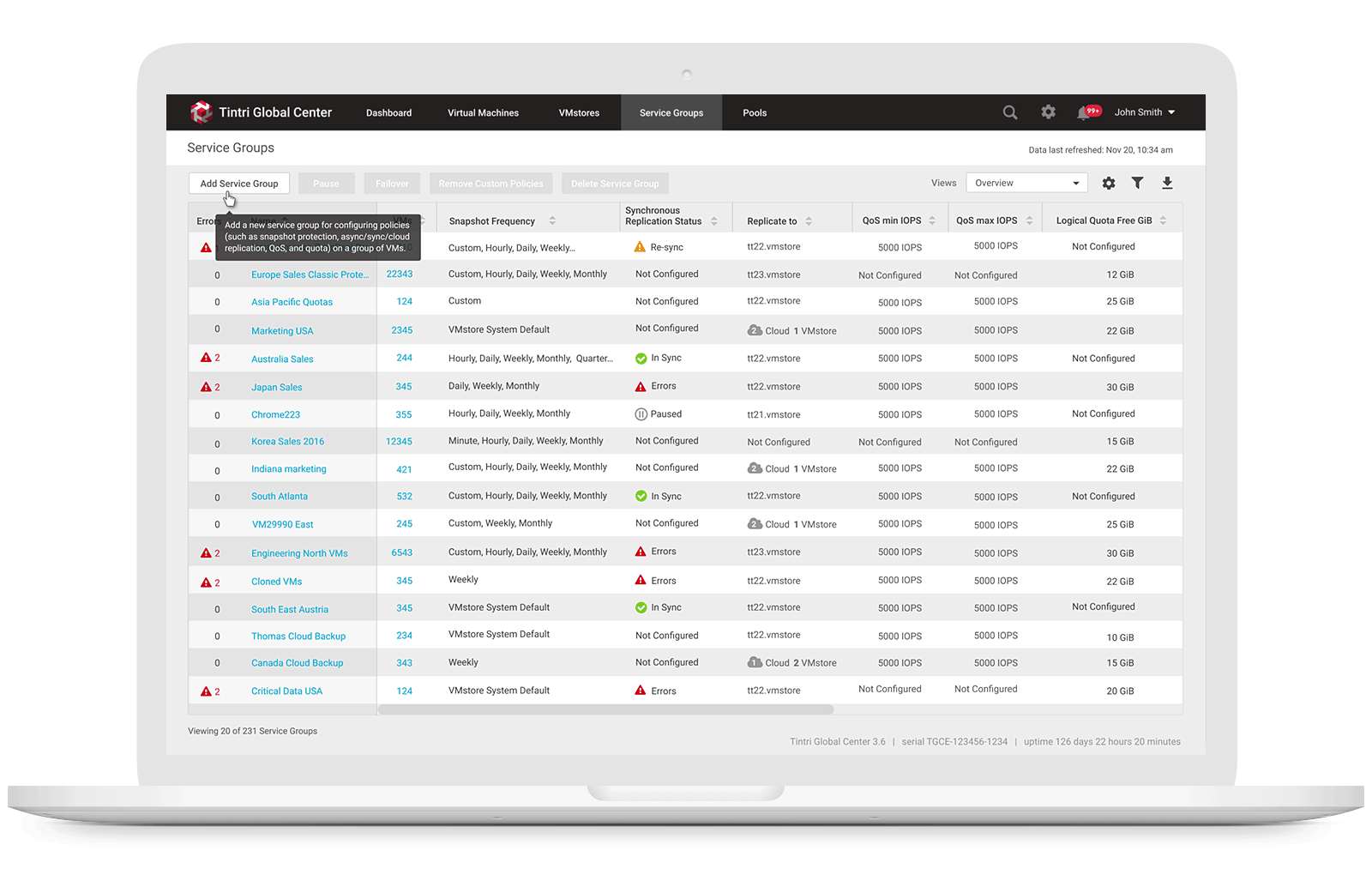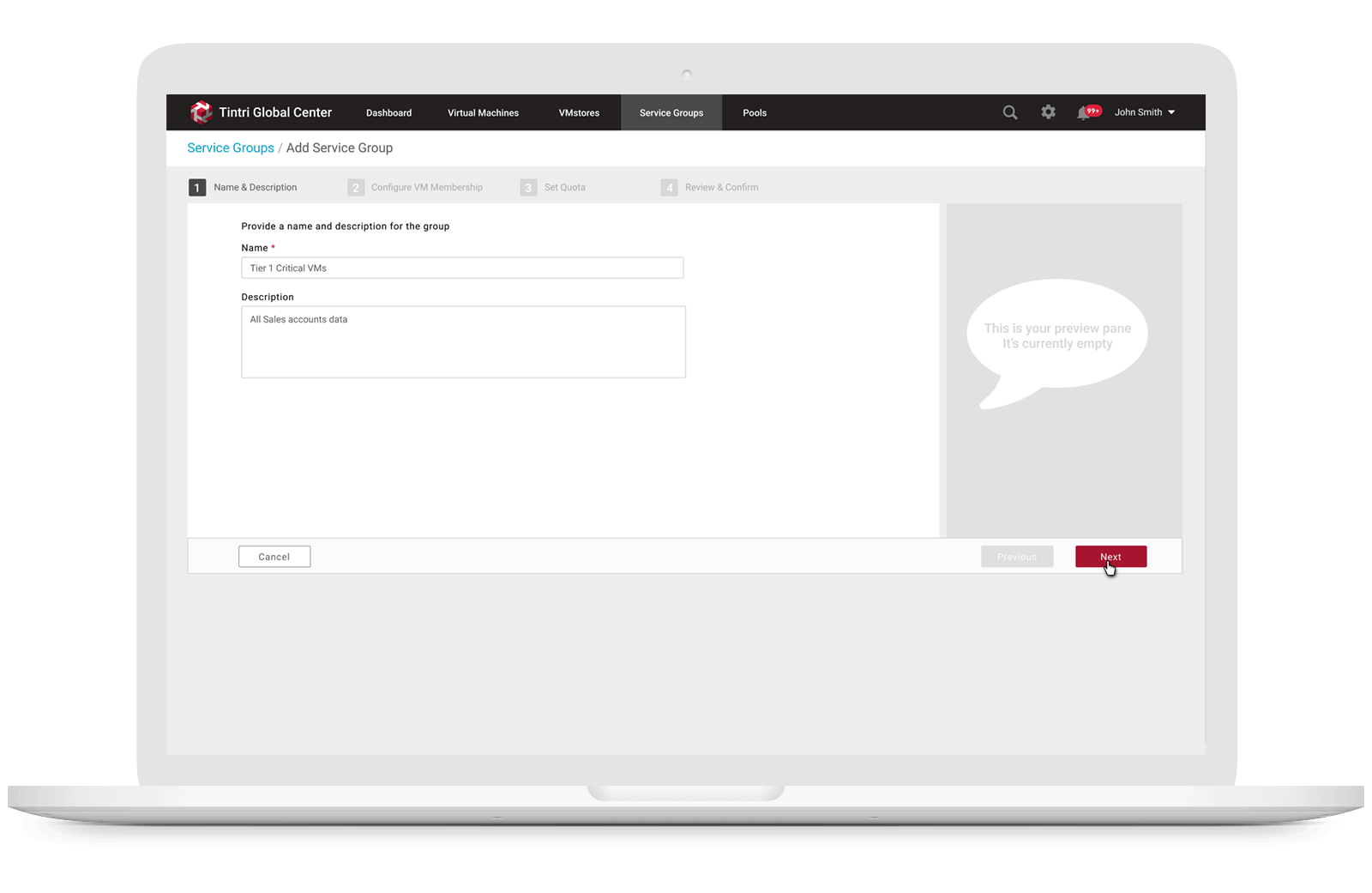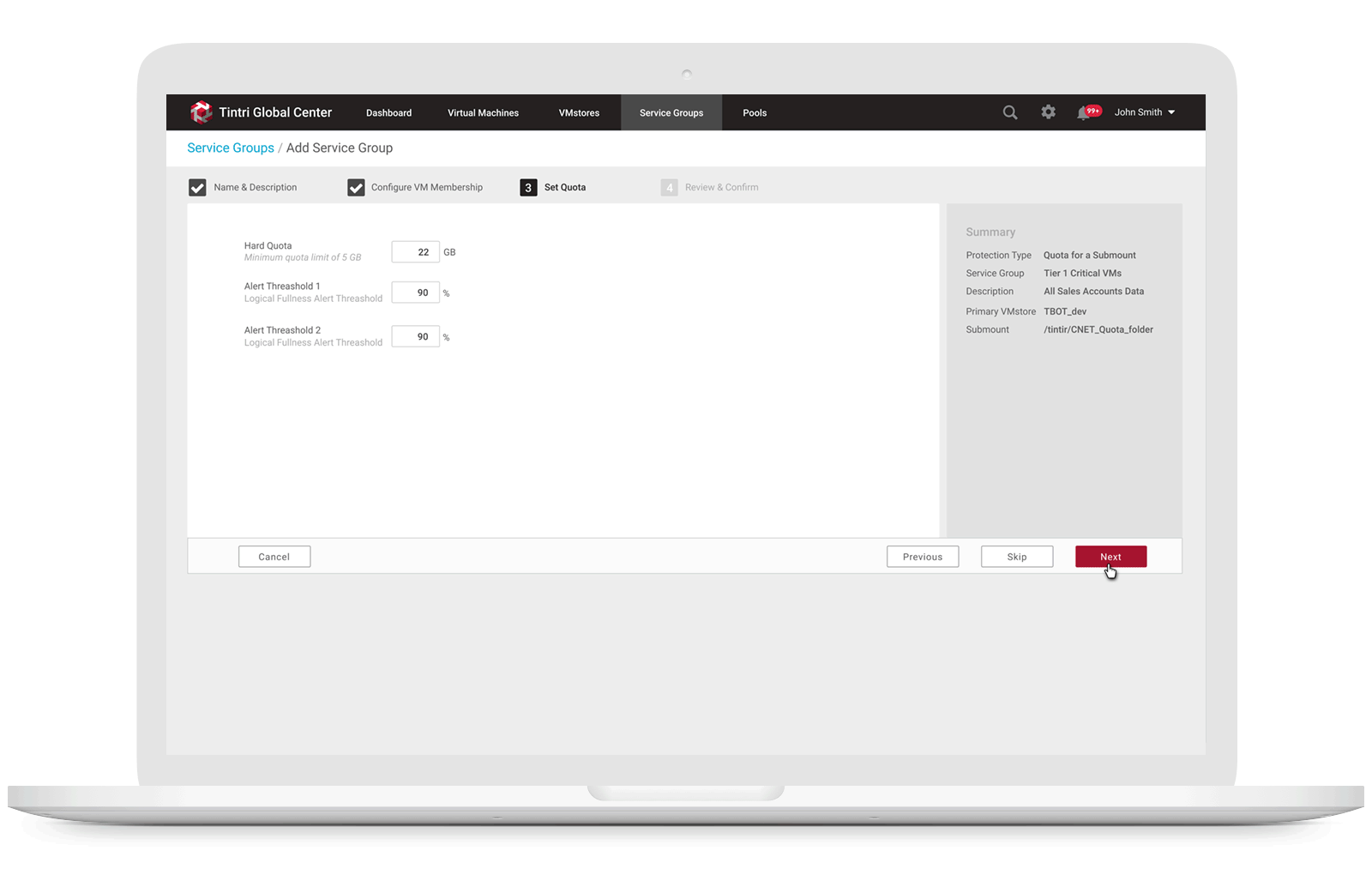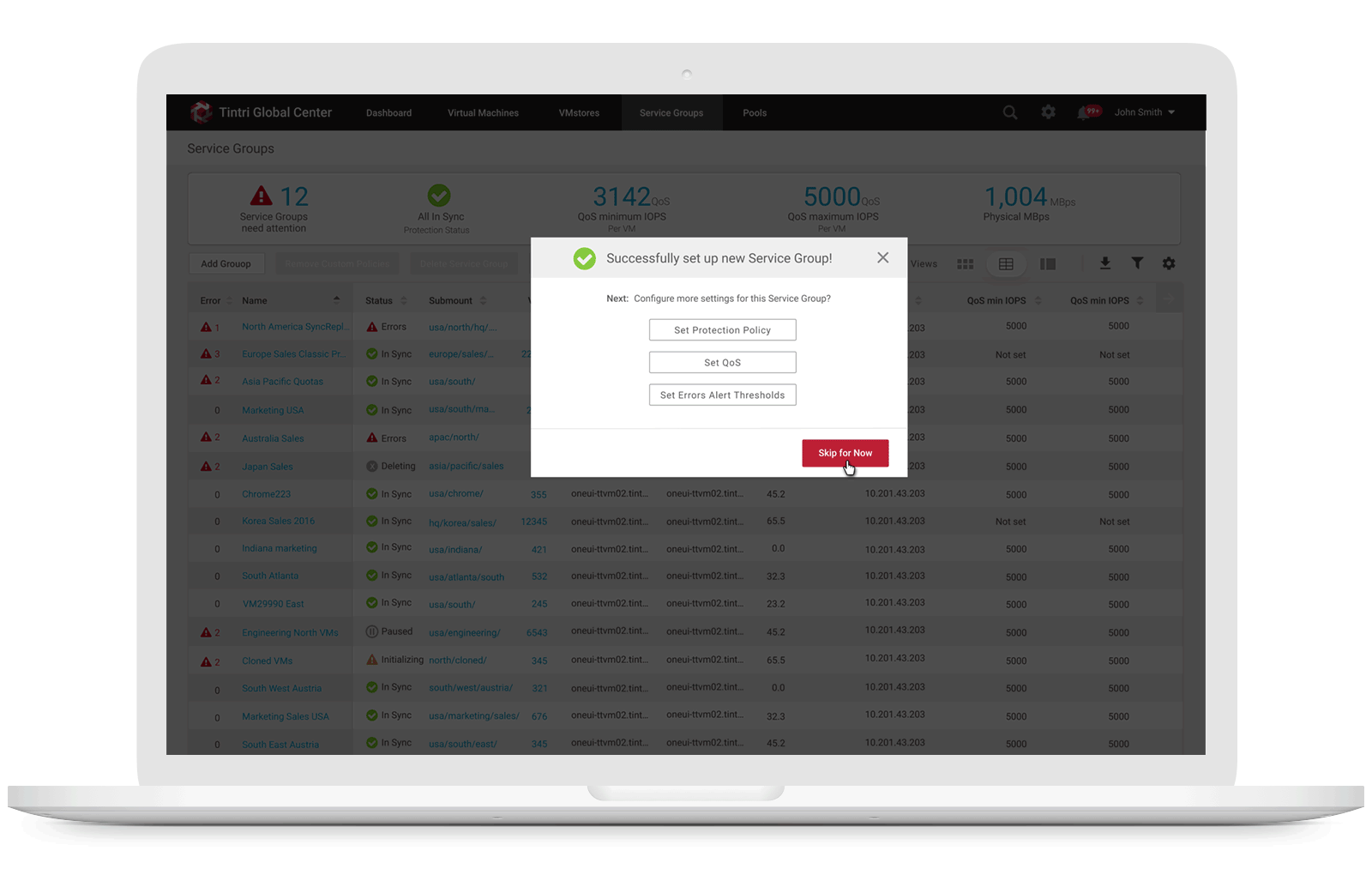
1. Allow storage engineers to create Service Group & set quota policy
Service Groups aggregate VMs that have common management needs. A multi-tenant environment is created through a combination of VMware vCenter configuration and service groups. A Service Group is used to group all of a tenant’s VMs, allowing common management of the associated storage. Part of that management includes the ability to specify a quota is to set up a multi-tenant environment, users need to create a Service Group for each tenant and assign each Service Group a hard quota. When they create a Service Group with a quota, a sub-mount is created automatically. A vCenter datastore can map to an entire Tintri array, or it can map to a sub-mount on an array, with or without a quota. Service Group creation is performed using Tintri Global Center (TGC). When users select the Service Groups tab and click on “add a Service Group,” they just need to provide a name and description for the group to create a Service Group with a quota:
2. Provided ability to modify storage usage quota
After creating a Service Group to monitoring space usage, users may modify quotas for the Service Group that they created along with data protection replication and QoS, if desired. When they select Edit in the Quotas section, they can then assign a quota in GiB, along with various alert thresholds.
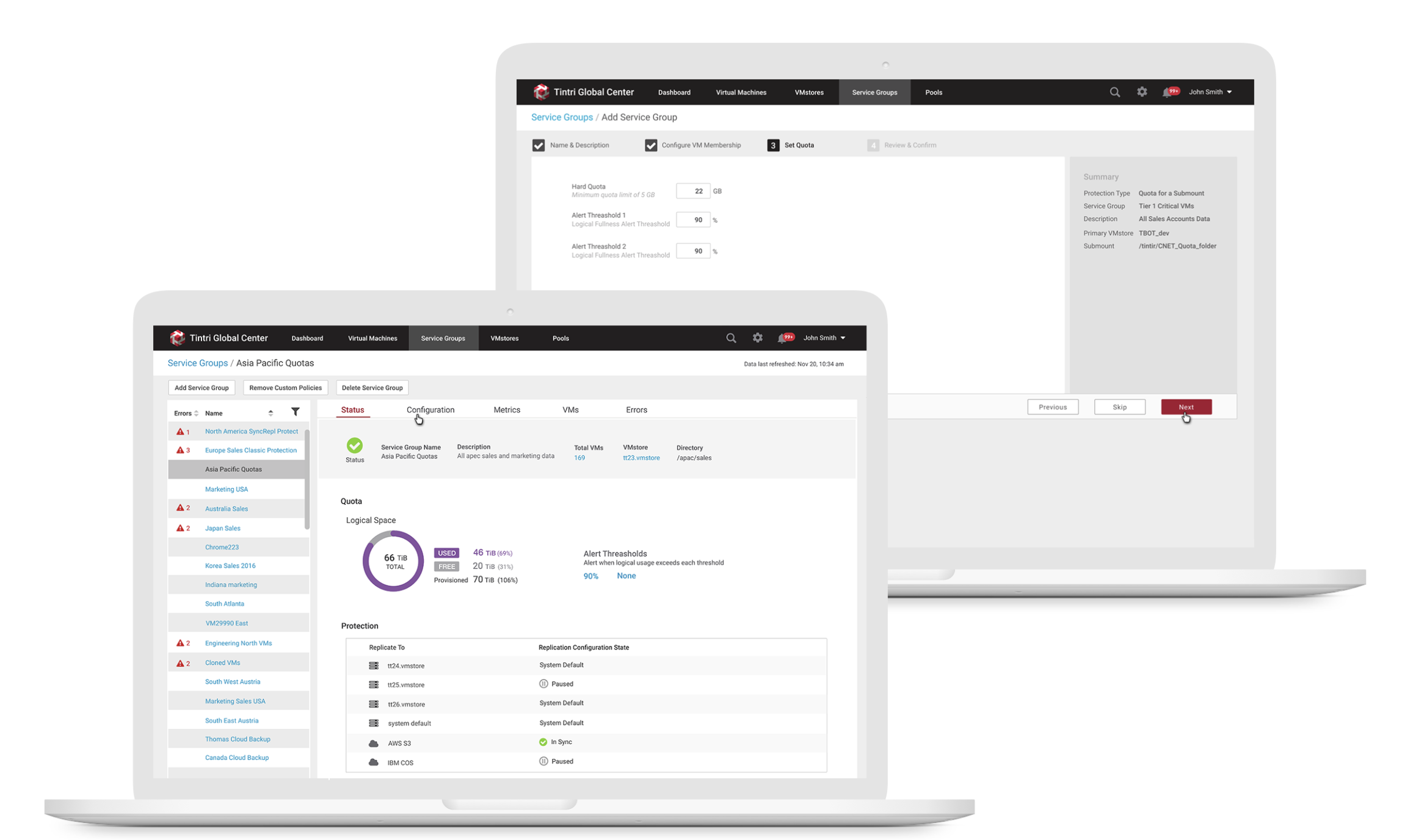
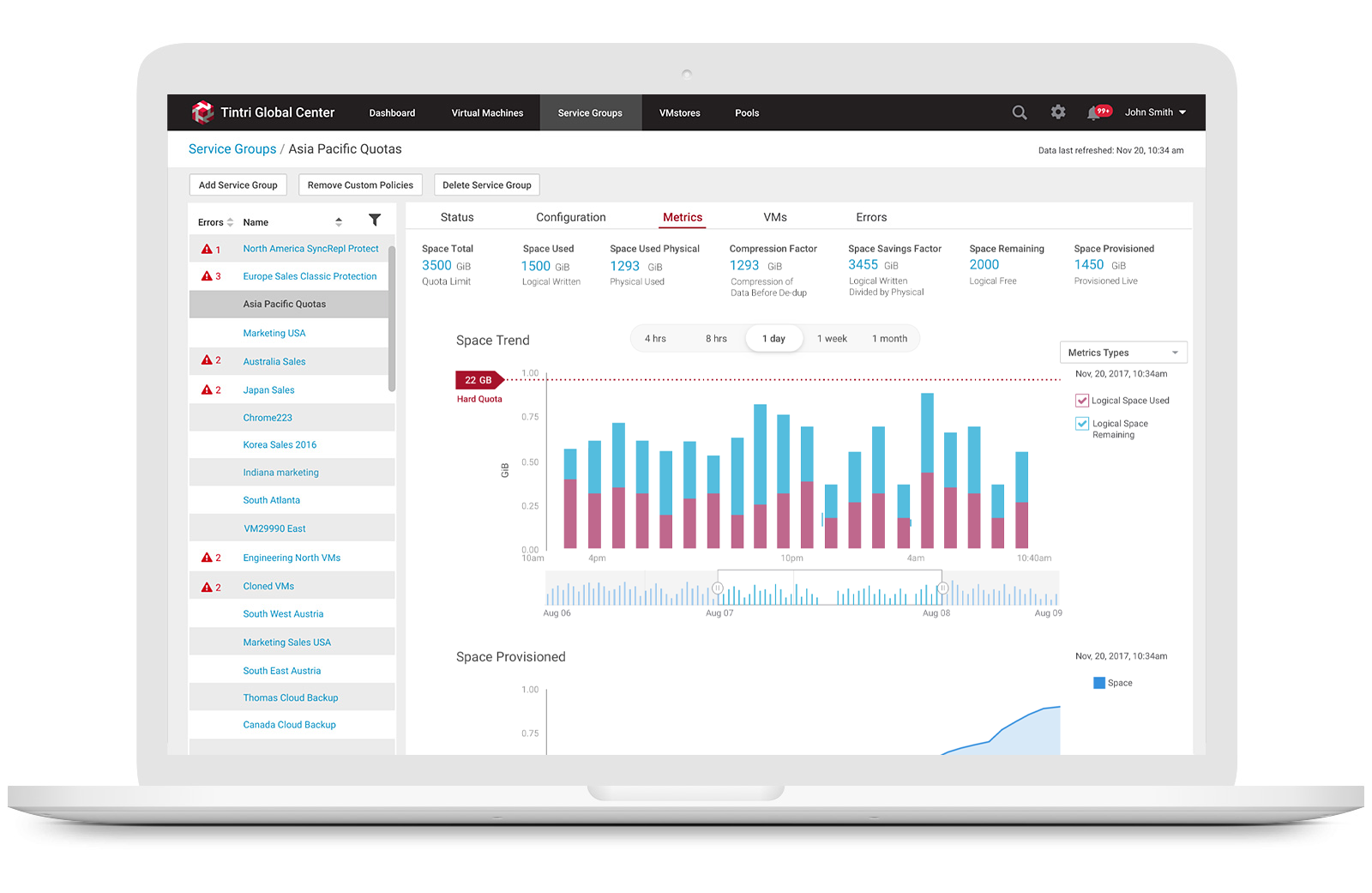
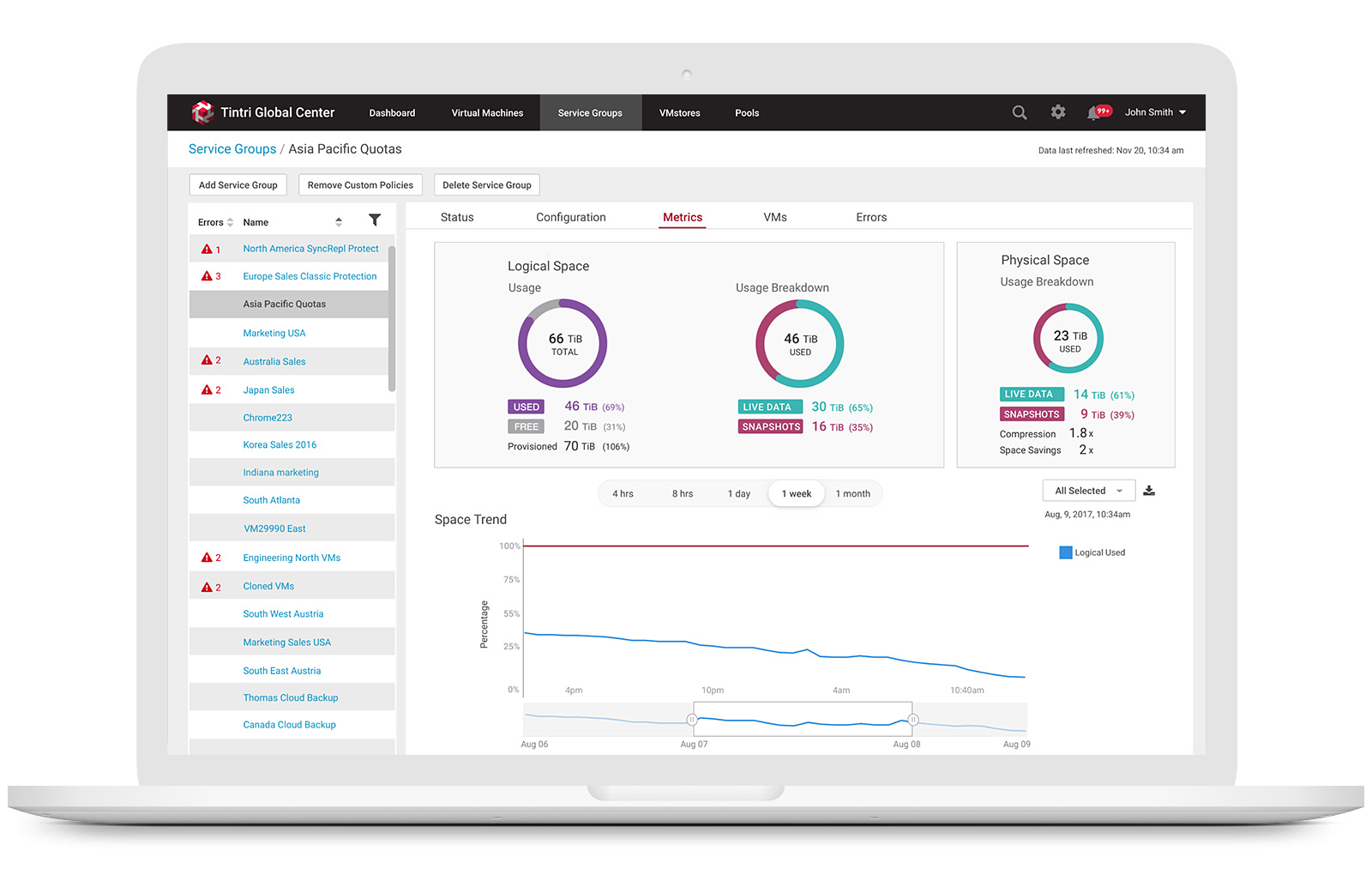
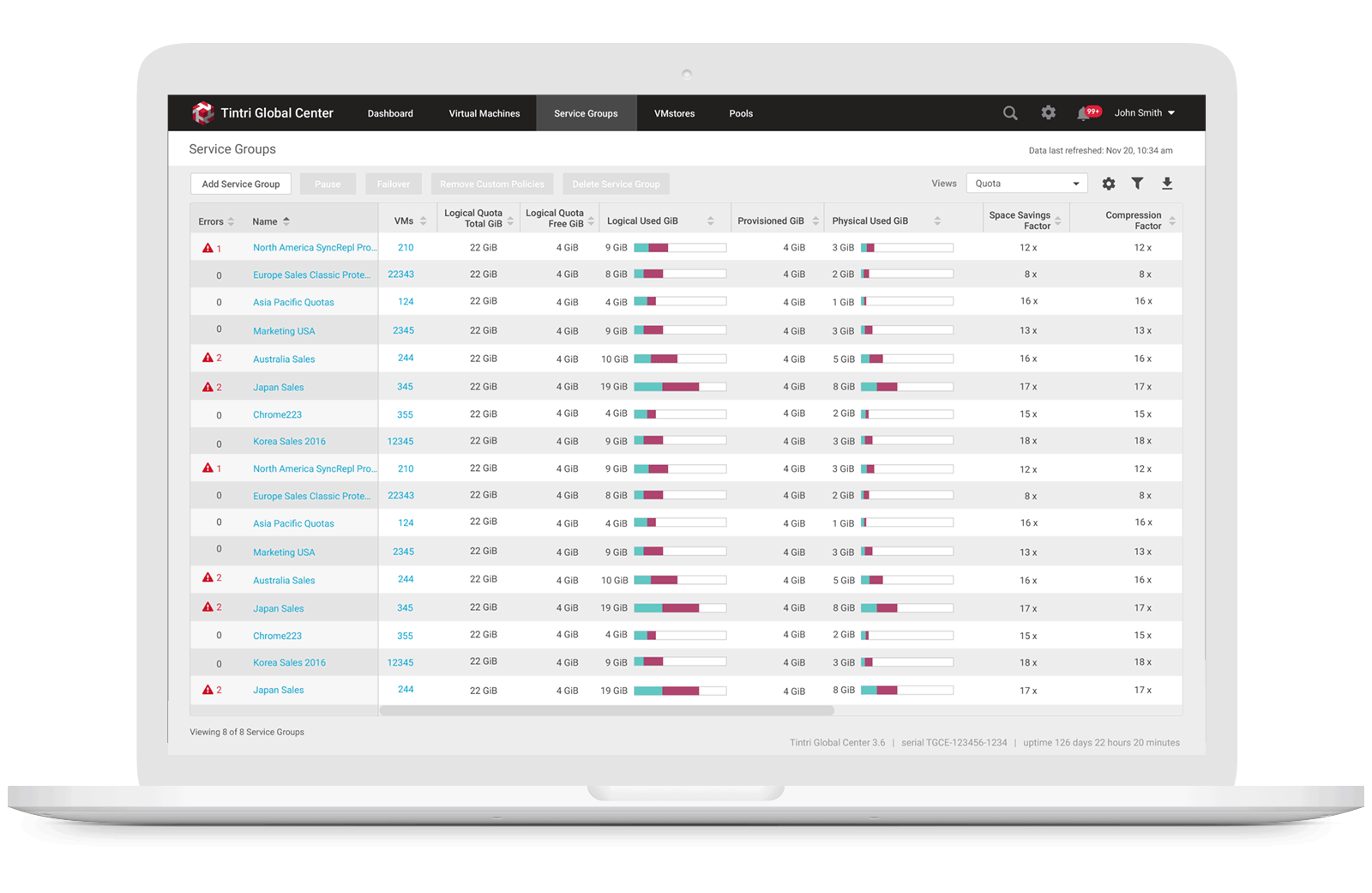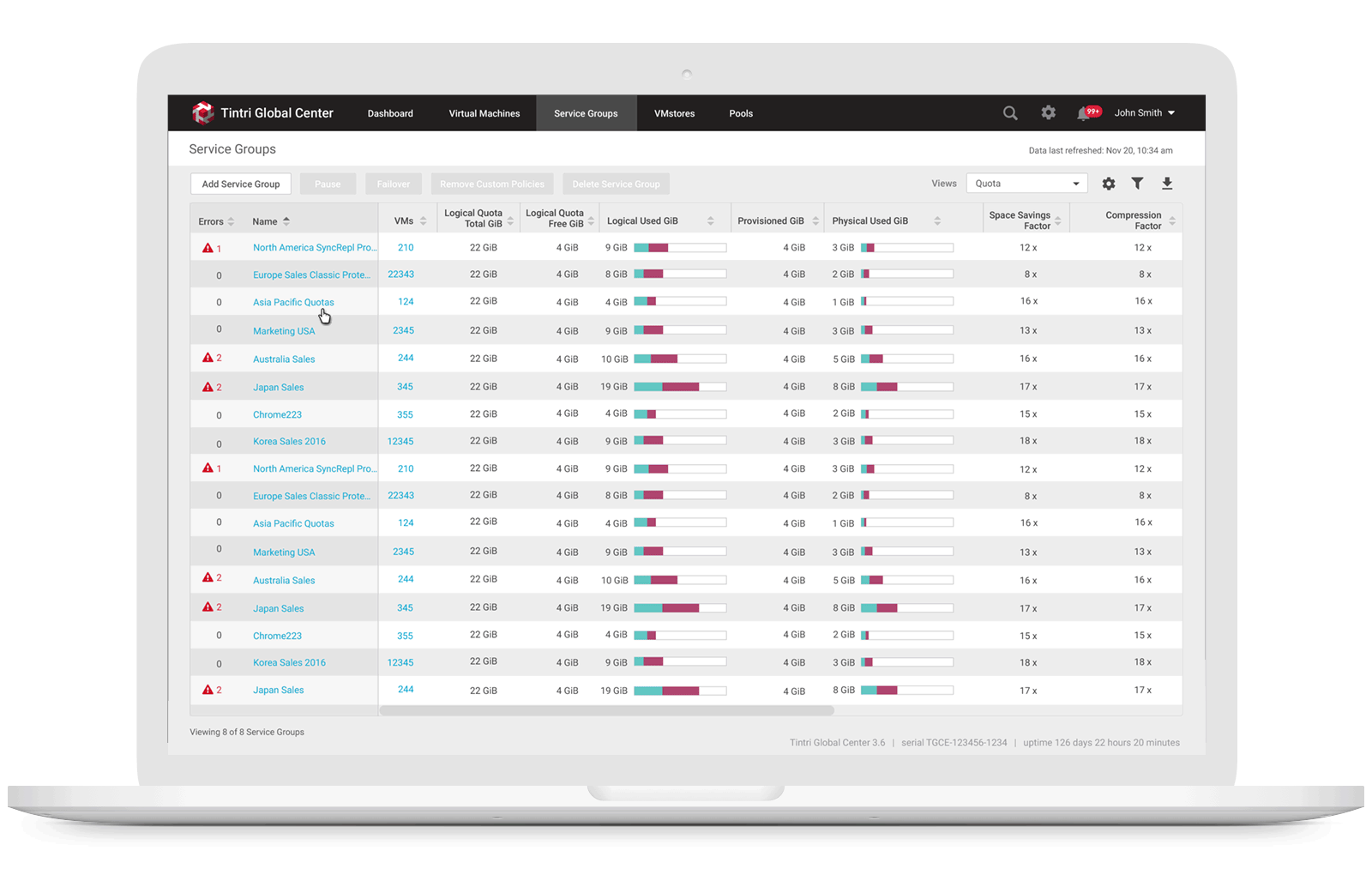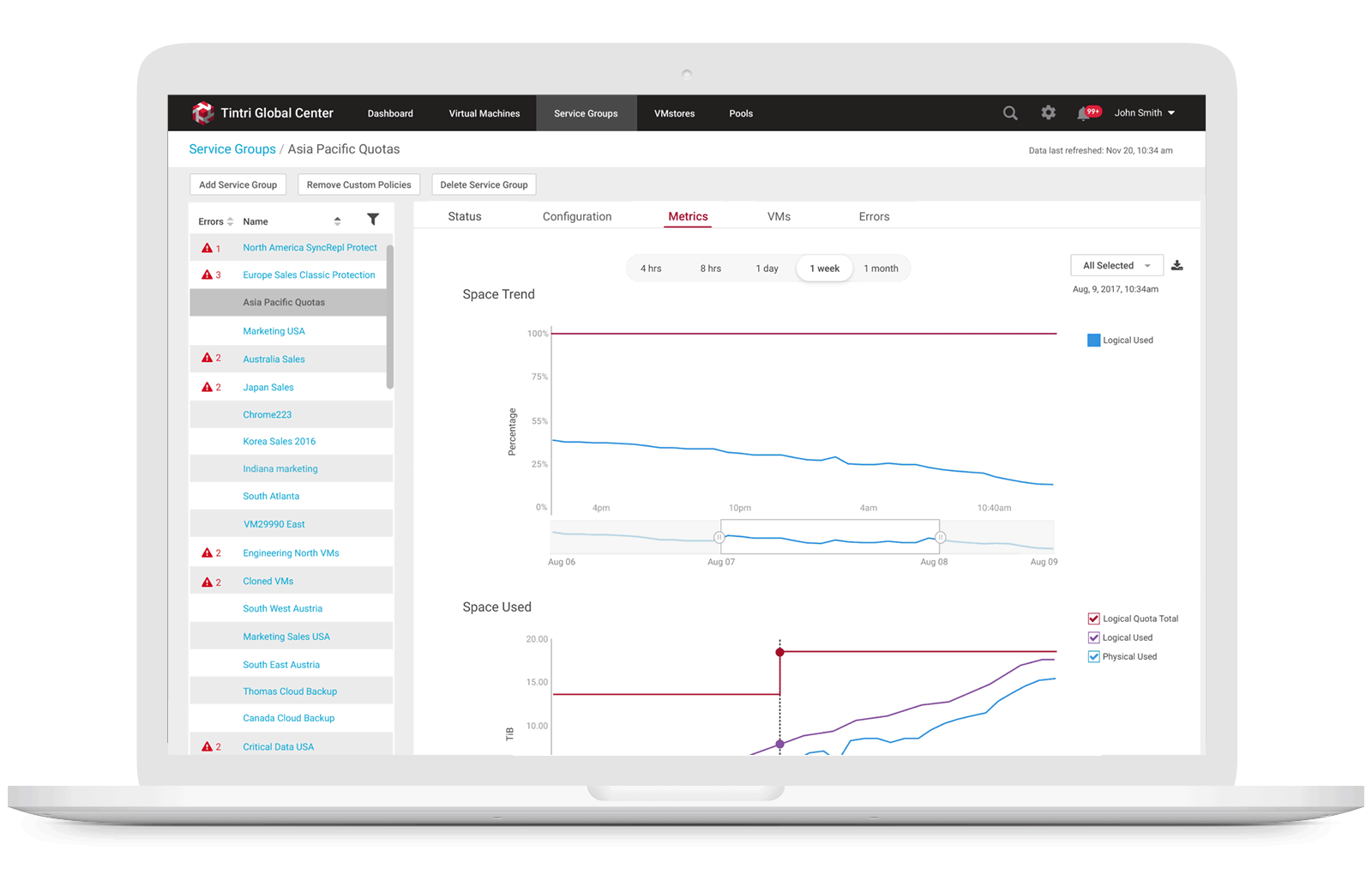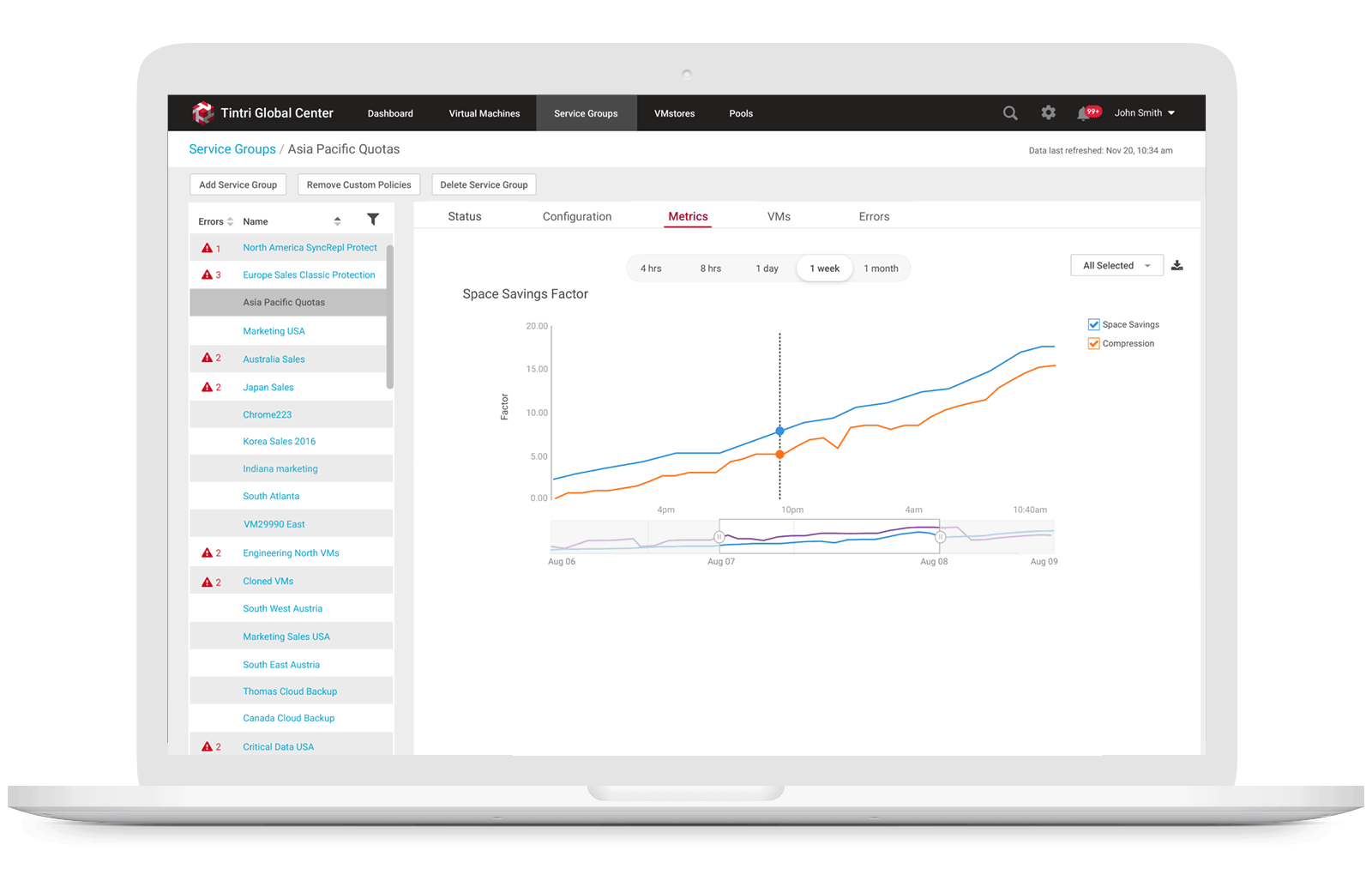
3. Allow storage engineers to monitor space usage trend
Users can view physical space and logical space usages of a specific Service Group from the list view or from a specific Service Group detail metrics view by selecting the Service Group Metrics tab, they can see logical space vs. physical space usage along with a variety of other graphs related to usage.